If you’re confused about why the microphone on your 3.5mm headset isn’t working properly on your computer, this article will provide you with practical solutions. Many users find that when they plug their headset with a built-in microphone into the headphone jack of their computer, the sound plays normally, but the microphone is not recognized. This article explains why that happens and how to fix it easily.
Understanding Different Types of 3.5mm Audio Jacks
First, it’s essential to recognize that not all 3.5mm audio jacks are identical. You can tell a lot about male 3.5mm plugs just from their appearance. They'll have one, two, or three black bands separating connections on the metal shaft. Modern headsets typically use a type called a TRRS (Tip-Ring-Ring-Sleeve) connector, whereas many desktop computers and older laptops are equipped with separate jacks for headphones and microphones, often utilizing TRS(Tip-Ring-Sleeve) connectors.
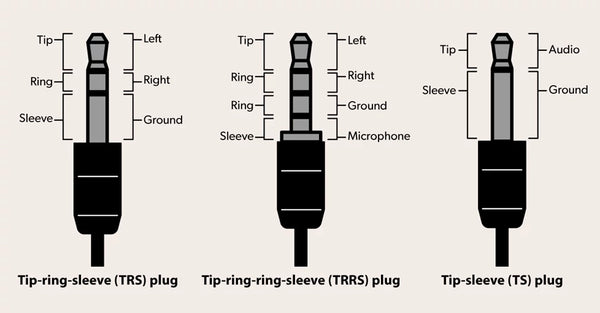
What Is a TRRS Connector?
TRRS stands for “Tip-Ring-Ring-Sleeve,” meaning the plug has four metal contact points separated by plastic rings. Specifically:
Tip: Left audio channel
First Ring: Right audio channel
Second Ring: Ground
Sleeve: Microphone signal
This type of connector is common in smartphones, modern laptops, and some all-in-one desktops. It combines both headphone and microphone signals into a single plug and cable.
What Is a TRS Connector?
TRS stands for “Tip-Ring-Sleeve” and has only three metal contact points:
Tip: Left audio channel
Ring: Right audio channel
Sleeve: Ground
This type of plug is usually used with the headphone jack on desktop computers, and the microphone usually has its separate input.
What Is a TS Connector?
TS (aka "mono mini") plugs have a tip for the audio signal and a sleeve for the ground. 3.5mm TS cables are often used for 12-volt trigger connections between audio components.
3.5mm headphone inputs
When you shop for 3.5mm cables and adapters, be sure you get the right plug for the jack you're connecting to.
How do you know which type of 3.5mm jack you have? Computers, tablets, and other devices often identify the connection with a pictogram.

Why Doesn’t My TRRS Headset Microphone Work on My Computer?
If you plug a TRRS headset (with microphone) into a TRS headphone jack on a computer, the audio will work, but the microphone will not. That’s because the TRS jack isn’t designed to receive a microphone signal; it lacks the necessary contact point to do so.
In short, even though the plug fits physically, the signal paths don’t match, so the microphone input can’t be transmitted or detected by the computer.
How to Fix TRRS Headset Microphone Issues on TRS Ports
Thankfully, the fix is quite simple: You need a TRRS-to-dual-TRS splitter.
This type of splitter separates the combined TRRS plug into two separate TRS plugs—one for audio output (headphones) and one for audio input (microphone). Here’s how to use it:
-
Plug your TRRS headset into the input end of the splitter.
-
Plug the TRS connector labeled “Headphone” into your computer’s headphone jack.
-
Plug the TRS connector labeled “Microphone” into your computer’s microphone jack.
This allows your computer to correctly recognize and use both the audio and microphone from your headset.
Special Case: Apple iPhone Headsets
Note that some Apple iPhone headsets use a different TRRS wiring standard. It’s been reported that their microphones may not work correctly with standard TRRS splitters because Apple uses a different pin configuration.
If you’re using Apple’s earbuds and want to use the microphone on a non-Apple device, it’s recommended to buy an adapter specifically designed for Apple products or use a different headset compatible with standard TRRS configurations.
Another Less Common Mic Input Issue
While the most common issue is using a TRRS headset in a TRS jack, there’s another case worth noting:
-
A user is using a professional XLR microphone connected to an audio interface.
-
The audio interface connects to the computer using a TRS to 3.5mm cable.
-
The computer’s jack is a TRRS combo port, which does not recognize the TRS mic input.
In this case, the solution is to use a TRS-to-TRRS adapter, converting the 3-contact plug to a 4-contact plug so the computer can properly detect the microphone input.
Conclusion
The root cause of headset microphone issues on computers often comes down to mismatched connector types. A TRRS headset plugged into a TRS jack won’t transmit the mic signal, rendering the microphone unusable. Thankfully, a simple splitter cable can resolve this issue.
Additionally, Apple headsets may require special adapters due to their unique wiring, and professional microphones using XLR may also need specific converters when used with TRRS combo jacks.
If you’re facing similar headset microphone problems, we hope this guide helps you find the right solution and get your devices working as expected.





